|
Does Attendance Matter?
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issue |
|
||
Student Numbers |
% (N=172) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Table 1: Attendance Statistics for MGMT389 (2005)
Table 1 shows that on average students attended 9.6 out of 12 or 80% of tutorials. However this needs to be considered in the context that students are required to attend 75% of tutorials or risk failing the subject . For lectures, where attendance is entirely voluntary, attendance was only measured for those who completed the survey. These students claimed their average attendance at lectures was 10.5 out of 13 classes or 81% of all classes. Once again we need to consider this result in context. The survey results are based on the 67% of students who attended the final Week 13 lecture. This lecture reviews the subject and provides information on the exam and, therefore, is traditionally the second most attended lecture, after the Week 1 lecture. These results compare with other research on attendance: Dolnicar (2004) found 80% average attendance at lectures across all Faculties but much less in the Faculty of Commerce; Rodgers and Rodgers (2003) found 62% at lectures and 73% at tutorials; Rodgers (2001); found 68% at lectures and 80% at tutorials; while Romer (1993) described absenteeism at elite United States colleges as 'rampant' with a 67% attendance rate.
In considering the significance of the attendance problem for MGMT389 in 2005, the only obvious difference between the MGMT389 class in 2005 and past years was the decreased attendance at lectures. Random class rolls conducted during the 2004 class lectures indicated an average attendance of 75%, better than in 2005. But it was not the decline in attendance that really bothered Massingham and led to this research study. Rather, it was his perception of an apathy and passiveness amongst the students in 2005. This group just did not seem as interested in learning as past years. In 2005, the result was a passive learning environment in both the lectures and the tutorials. In the lectures, attempts to engage the students in discussion using various interactive techniques, often fell flat. Only a small number of students were willing to engage in discussion and this group were often reluctant to speak from fear of being seen as 'opinionated' or 'know-it-alls' by their peers. Massingham wondered why many students were unwilling to attend class and engage in the learning process. He suspected that the non-attendees did not see any value in attending class and wondered why. In looking for answers, the only obvious factors were the introduction of on-line access to the audio of lectures (eduStream) and the students themselves.
It was tempting to blame eduStream for the declining attendance in 2005 because it provides students with an easy option to miss lectures. However, we will see later in this article (see Table 2) that eduStream was not a significant factor. Indeed, its rating is similar to that for 'I didn't like the lecturer', so Peter can only blame the technology as much as himself! When we consider this point, the only other difference was the students themselves. Were they different compared with previous years? Or was their motivation more readily influenced by some other factor, such as the process or the lecturer? Before exploring these questions, Massingham considered whether student attendance really mattered at all and, if so, how this could be measured.
The most objective way of answering whether student attendance matters is the relationship between student attendance and performance. Recently, researchers have begun to empirically test whether absenteeism from university classrooms has a consequent effect on student learning (see Devadoss and Foltz, 1996; Marburger, 2001; Rodgers, 2001; Rodgers and Rodgers, 2003). Much of this research reports a strong association between attendance and performance but not a statistically sound causal relationship. Durden and Ellis (1995) found that excessive absenteeism impacted on the performance of economics students. Rodgers (2001) found a 'small but statistically significant' effect on performance, Rodgers and Rodgers (2003) claim to have found 'strong support for the proposition that class attendance has a significant effect on academic performance'. Our paper extends this research by examining the reasons why students do not attend classes and linking this to performance.
The aim of the research was then to examine student absenteeism from university classes. The specific research questions were:
- What are the perceived reasons for non-attendance at university classes?
- What relationship exists between perceived attendance and performance?
- What relationships exist between the depth (class participation) and breadth (attendance) of student involvement in the learning process and student performance?
Research Method
The Case Study
The study was conducted at the completion of the autumn session 2005 at the University of Wollongong. The data was collected from a survey of a class of 172 students from the Faculty of Commerce, who completed a third year undergraduate subject. The class met for a two hour lecture and a one hour tutorial per week over a 13 week session. Lectures were delivered to the whole class and tutorials were given to seven groups ranging from 20 to 30 students each. The same lecturer (Massingham) delivered the lectures and the tutorials were shared between the lecturer and a tutor.
The survey took place at the start of the Week 13 lecture. This is traditionally a lecture where most students attend because it includes a discussion of the forthcoming exam. The surveys were distributed and the process was explained to students. Students were not required to identify themselves on the survey in order to ensure responses that were honest and not biased for fear of recriminations. Appendix 1 provides a list of the survey questions.
Assessment for the subject consisted of five components: a case study (15 per cent), research paper (20 per cent), mid term exam (10 per cent), class participation (5 per cent), and final examination (50 per cent). All assessments were double marked if students failed. The lecturer marked all of the exams to ensure consistency across the subject.
All assessments were directly related to content covered during the lectures and students were informed of this throughout the session. We controlled for bias towards students with high attendance rates over those with low attendance rates, in the following way:
- All students had equal access to the subject's learning resources (e.g. subject outline, text book, additional readings in the library,
and power-point slides from the lectures that were placed on WebCT intranet).
- All students had equal access to the lecturer and tutor during classes and after class during consultation times.
- All students had the opportunity to download the audio of the lectures from the intranet (eduStream).
- The final examination was graded without any reference to the identity of the student (i.e. the front page, which includes the name and student number, was not referred to until the final grade for the student had been concluded).
The only learning component not directly available to students who missed classes was the opportunity to ask questions and otherwise involve them in the class discussion. Given that non-attendance was their choice, we believe that students had equal access to the examinable content in the subject.
Of the 172 students who completed the subject, 115 (67 per cent) attended the final Week 13 lecture and completed the survey. However, we had data on all 172 students in terms of their attendance at tutorials because enrolment records were maintained. We also had performance data on all 172 students. Therefore, we could examine the performance of all students in terms of their attendance. However, we could examine the attitudes towards attendance, that is, the survey, for the 115 students only.
Breadth and Depth of Learning
Measures of breadth and depth of learning were developed as a proxy for student involvement in the learning process. Breadth was measured in terms of student attendance, while depth was measured in terms of class participation.
Students were classified into three groups based on the breadth of their attendance. This was derived from each student's average overall attendance: Poor (attended 9.5 classes or less), Satisfactory (attended 10 to 11 classes), and Good (attended 11.5 to 12.5 of classes). The average was calculated by adding the number of lectures and tutorials attended and dividing by two. The maximum is 12.5 because there were 13 lectures and 12 tutorials. Descriptive statistics for each band are presented in Table 2
|
Mean |
Standard |
N |
|---|---|---|---|
All |
10.5 |
1.6 |
115 |
Good (>11 classes) |
12 |
0.4 |
41 |
Satisfactory (10-11 classes) |
10.6 |
0.4 |
41 |
Poor (<10 classes) |
8.2 |
1.2 |
31 |
Table 2: Descriptive Statistics for Class Attendance (i.e. breadth of attendance).
Students were classified into three groups based on the depth of their learning. This was derived from their level of class interaction and participation. We allocated students a Class Participation Grade (CPG) (maximum 5) based on the quality and quantity of their involvement in class discussion. We classified students into the following three groups based on their Class Participation Grade: Poor (<3), Satisfactory (3 to 4), and Good (4 to 5). Descriptive statistics for each band are presented in Table 3. Student attendance was a contributing factor in determining the CPG. For example, a student who attended all classes and actively contributed to the learning process, through useful questions and comments, would achieve a higher CPG than a student who equally contributed but attended less classes. The former student contributes more, overall, to the learning process and is rewarded with a higher CPG. Further details explaining how CPG were derived is provided in Appendix 2.
|
Mean |
Standard |
N |
|---|---|---|---|
All |
3.5 |
0.9 |
115 |
Good (4-5) |
4.4 |
0.4 |
35 |
Satisfactory (3-4) |
3.5 |
0 |
50 |
Poor (< 3) |
2.5 |
0.9 |
30 |
Table 3: Descriptive Statistics for Class Participation Grade Score.
It might be argued that CPG is an inadequate measure of depth of learning for several reasons. First, students might decide to forgo the opportunity to obtain 5 marks from this assessment for reasons explored in the results section of this article. For example, they may have been too busy to attend tutorials or to prepare for those tutorials they did attend. As a result, they might only be able to sit passively in class and, therefore, would receive a low CPG. Second, some students might lack the motivation or skills to engage in class discussion. They may still be learning through processes of listening and observation but their depth of learning would not be reflected in the CPG because they do not visibly demonstrate their learning. Despite these criticisms, we felt that CPG was an adequate measure of depth of learning because it allows us to observe whether students are engaged, understand, and can articulate this understanding with some level of insight. Further support for this approach is based on the fact CPG is an assessment task that is explained to students at the start of the tutorials, i.e. there is a reward for the desired behaviour.
Student Attitudes Towards Attendance
We surveyed the reasons for non attendance by providing respondents with a list of statements explaining reasons for non-attendance. Appendix 1 provides further details. Respondents were asked to rate their agreement with each statement using a using a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = not sure, 4 = agree, and 5 = strongly agree. The responses were aggregated and divided by the sample size to derive mean scores for each statement.
Student Performance
In relation to performance, students were classified into three groups, depending upon their final grade for the subject: Good (grades of 75% or higher), Satisfactory (grades of 50-74%), and Poor (grades below 50%). Descriptive statistics for each performance band are presented in Table 4
|
Mean |
Standard |
N |
|---|---|---|---|
All |
62.2 |
14.1 |
115 |
Good (≥75%) |
79.3 |
4.1 |
28 |
Satisfactory (50-74%) |
61.2 |
6.5 |
70 |
Poor (≤50%) |
36.7 |
6.1 |
17 |
Table 4: Student performance by classification band.
Results
Introduction
The results are presented as follows. First, we present the reasons why students do not attend lectures and tutorials. This addresses the first research question. Second, we examine differences in attitude towards attendance between good, average, and poor students. This addresses the second research question. Third, we explore whether the depth and or breadth of student involvement in the learning process influences student performance. This addresses the third research question.
Reasons for Non-attendance by Attendance and Participation Ratings
Table 5 shows the mean response for each questionnaire item for all students who responded to the questionnaire. The 95% confidence interval for the mean is shown for each performance group - both for attendance and participation ratings.
Cells with shading indicate a significant difference between the groups (Kruskal-Wallis test for independent samples p < 0.0125 - bonferroni corrected 0.05 _2df=2> 13.4). Where two cells within each shaded block are in bold and italic these groups appear to differ significantly from each other. Where a single cell is in bold and italic this group differs significantly from both other groups. Potentially significant differences between groups are assessed by identifying that groups' 95% confidence interval do not overlap with each other.
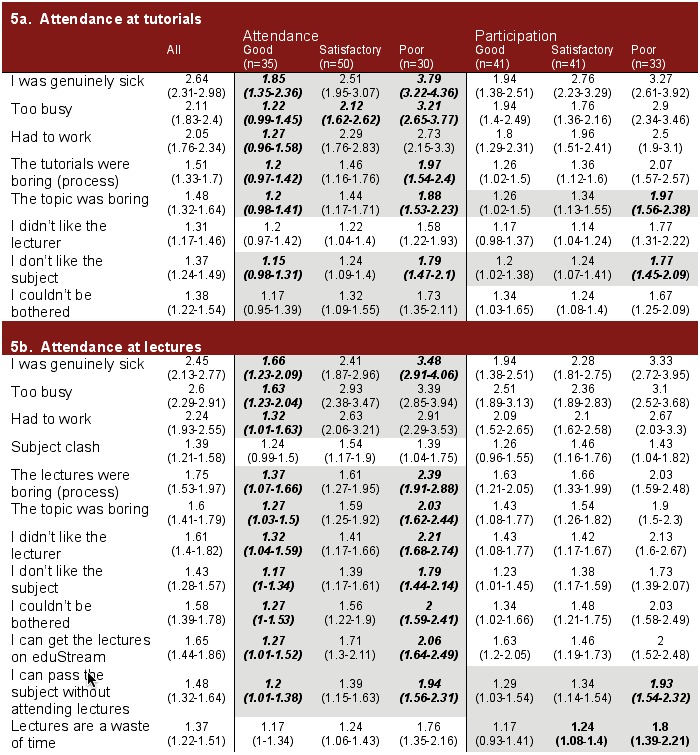
Table 5: Mean score for questionnaire item
(range of 95% confidence interval in parentheses).
Statistical Procedure
A Kruskal-Wallis independent samples test (non-parametric equivalent of the one-way analysis of variance) was performed for each question to see if there was a significant difference in response between the different participation and attendance bandings. As this results in 40 different comparisons of the same data set the Bonferroni correction was applied to the p value (0.5/40 = 0.00125) and the questionnaire items for the individual were then compared by examining the overlap of the 95% confidence intervals by hand. Significant items are highlighted in table 5 and the significant differences within each group are presented in bold italic.
Reasons for Tutorial Non-Attendance by Attendance and Participation Ratings
Table 5a summarises these results. For the attendance grouping all questions excepting "I dislike the lecturer", and "I couldn't be bothered" resulted in significant differences, and for the participation grouping "the topic was boring" and "I don't like the subject" were the only two questions with significant differences. Overall, sickness, busyness and work were by far the source of the largest differences with the remaining significant questions showing about the same differences. Therefore, lifestyle factors had the most influence on breadth of learning (i.e. attendance at tutorials), while motivational factors had the most influence on depth of learning (i.e. participation at tutorials).
Reasons for Lecture Non-Attendance by Attendance and Participation Ratings
Table 5b summarises these results. All questions except "subject clash" and "Lectures are a waste of time" showed significant differences for Attendance ratings. When examining the differences by participation, only "I can pass the subject without attending" and "Lectures are a waste of time" were significant.
For Attendance, the largest effects are seen for the sickness, busy and work questions followed by "the lectures were boring" and "I can pass the subject without attending", thus questions pertaining to motivation. The other differences are much smaller. It was interesting to note that the motivation related questions were much more important for lectures than tutorials, perhaps indicating that motivational factors are of greater importance for non-compulsory classes compared to compulsory classes.
For Participation the differences are small - extremely small for the "lectures are a waste of time" question where no pattern emerges in the secondary analysis. Again this highlights the importance of motivational related questions. The results indicate that Participation rating is a much poorer grouping measure than Attendance.
Reasons for Lecture Non-Attendance by Performance
Table 6 summarises the median and inter-quartile range (median ± IQR = range of 75% of the obtained values) for each questionnaire item. There was no significant difference between the different performance groups on the answers to the questionnaire. A Kruskal-Wallis test of the significance of the difference between the median answer for each group resulted in no questionnaire item showing significant differences. This indicates that academic performance does not determine the answer to each question. However, it must be noted that there was much less variability for the "Good" group, with at least 75% of the sample choosing the same answer for every question than the other two groups. Being that the questions are generally couched in negative terms and each item is marked "Strongly Disagree" by a firm majority of the 'Good' group, this indicates a more unanimous positive view of the lectures for this group than the rest of the questionnaire sample.
Reason |
All |
Good |
Satisfactory |
Poor |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I was genuinely sick |
1 (3) |
1 (0) |
1 (3.5) |
4 (3) |
|
Too busy |
2 (3) |
1 (0) |
3 (4) |
4 (3) |
|
Had to work |
1 (3) |
1 (0) |
1 (4) |
2 (4) |
|
Subject clash |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
|
The lectures were boring (process) |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
2 (2) |
|
The topic was boring |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
2 (2) |
|
I didn't like the lecturer |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
2 (3) |
|
I don't like the subject |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
1 (1) |
|
I couldn't be bothered |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
2 (2) |
|
I can get the lectures on eduStream |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
2 (2) |
|
I can pass the subject without attending lectures |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (0.5) |
2 (2) |
|
Lectures are a waste of time |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
Table 6: Why Students Miss Lectures by Performance
- Median response / 5 (Inter-quartile Range)
Reasons for Tutorial Non-Attendance and Performance
Table 7 provides an analysis of the reasons students miss tutorials by level of performance in the subject, using the same method as Table 6.
Reason |
All |
Good |
Satisfactory |
Poor |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I was genuinely sick |
1 (4) |
1 (0.5) |
1 (4) |
5 (2.5) |
|
Too busy |
1 (3) |
1 (0) |
1 (3) |
4 (3.5) |
|
Had to work |
1 (3) |
1 (0) |
1 (3) |
3 (3) |
|
The tutorials were boring (process) |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
1 (2) |
|
The topic was boring |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
2 (2) |
|
I didn't like the tutor |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
|
I don't like the subject |
1 (1) |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
2 (1.5) |
|
I couldn't be bothered |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (0) |
1 (1) |
Table 7: Why Students Miss Tutorials by Performance Level
- Median response (Inter-quartile range)
Table 7: Why Students Miss Tutorials by Performance Level - Median response (Inter-quartile range)
As with lecture attendance and performance, there is no significant difference between the groups when tested with a Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric analysis of variance. In general the pattern is similar to the attributed reasons for lecture non-attendance with the 'Good' group being almost as unanimous for tutorials as lectures, thus representing a more positive view of the teaching process for lectures as well.
The Timing of Classes, Absenteeism, and Performance
There was anecdotal evidence that the time of classes had an impact on student attendance. For example, classes scheduled on Fridays or Thursday nights are notoriously poorly attended. Given the findings that work commitments are an important reason for student absenteeism, we decided to examine whether there was a relationship between timing, absenteeism and performance. The analysis provides several findings. First, the lowest average attendance at lectures was the tutorial immediately following the lecture (tutorial 3) and the late evening class on Tuesday (tutorial 5). Tutorial 5's attendance supports the working student hypothesis. This late class is usually chosen by part-time students who work during the day and, therefore, are more likely to miss the lecture which is held during the day. However, Tutorial 3's attendance tends to disprove the proposition that time is important to attendance. This group immediately followed the lecture and, therefore, it is reasonable to assume that they would have the best opportunity to attend the lecture. This point is further supported by the fact that attendance at other tutorials held at far less popular times (e.g. 8.30 am) were better attended than Tutorial 3. This suggests that time may not be an influential factor and that we might look closer at the attitudes of the Tutorial 3 students, in particular, to identify the real cause of absenteeism. When we examined the factor ratings of the Tutorial 3 students, we found two important results. First, this group had stronger feelings of dislike about the teaching process (mean score of 1.82 compared with 1.51 for all students) and the lecturer/tutor (mean score of 1.95 compared with 1.61 for all students) compared with other tutorial groups. Second, there were a higher proportion of poor performing students in the group (32% compared to 24% for the whole class).
Student Attendance by Performance
We examined whether differences in attendance had an influence on student performance in the subject in two ways: breadth (average attendance) and depth (class participation grade) of learning. Tables 8 and 9 present the details of this analysis.
|
χ2df=4=15.7 p<0.01 |
Final Grade Rating |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Good |
Satisfactory |
Poor |
|
Attendance rating |
Good |
11 |
27 |
3 |
|
Satisfactory |
11 |
28 |
2 |
||
Poor |
6 |
15 |
12 |
||
Table 8: Contingency Table of Final Performance against Attendance Rating
Table 8 shows that increased attendance clearly has an effect on performance. Good and satisfactory attenders were more than twice as likely to be in the "Good" band for the final grade compared to poor attenders, and were much less likely to be in the Poor performance band.
The results are even clearer when we consider the 'depth' of student participation in the learning process, i.e. class participation grade (CPG), and performance. Only 1 "Poor" CPG student received a "Good" final grade, and very few "Good" and "Satisfactory" CPG students received a "Poor" final grade. This provides a clear finding that engagement in the learning process is much more important to student performance than mere attendance. The increased _2 statistic for Participation versus Final Grade compared to Attendance versus Final Grade is clear evidence for this (see Table 9).
|
χ2df=4=67.5 p<0.01 |
Final Grade Rating |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Good |
Satisfactory |
Poor |
|
Participation rating |
Good |
22 |
15 |
3 |
|
Satisfactory |
8 |
48 |
9 |
||
Poor |
1 |
33 |
33 |
||
Table 9: Contingency Table of Final Performance against Participation Rating
Conclusions
This article contributes to our understanding of the reasons for student non-attendance at University classes. Our research objective was to understand student motivations so that we might find ways to better engage students in the learning process. University students include as their main reasons for not attending lectures and tutorials as being: busy, sick, at work, bored, having technology alternatives (eduStream), and the teacher. When there are no health and lifestyle factors involved, the most important influence on attendance is student attitudes to learning and motivation, such as "the topic was boring" and "I don't like the subject".
For classes considered compulsory (e.g. tutorials in this case), lifestyle factors had the most influence on breadth of learning (i.e. attendance at tutorials), while motivational factors had the most influence on depth of learning (i.e. participation at tutorials). This means that health and lifestyle factors are barriers to tutorial attendance and lack of interest or motivation are barriers to tutorial learning. It was interesting to note that the motivation related questions were stronger factors for missing lectures compared with tutorials, perhaps indicating that motivational factors are of greater importance for non-compulsory classes compared to compulsory classes.
The main factors influencing student attitudes are the teaching process used (i.e. motivating versus boring; constructivist versus transmissive; authentic versus theoretical) and the teaching style and personality of the teacher. Learning is a social construct and the relationship between teacher and student appears to be a significant factor in the breadth and depth of student involvement in the learning process and the learning outcomes. These points were particularly supported by the findings on lecture attendance, which is a 'voluntary' decision for students, rather than tutorials, which are perceived as necessary due to attendance requirements.
For lectures, there is clearly a group of students who do not attend because they feel they "can pass the subject without attending", "Lectures are a waste of time", and "the lectures were boring". However, it is important to note that there were few significant differences in attitudes towards lecture attendance by participation (i.e. CPG). This means that differences in attitudes towards lecture attendance are explained by breadth of learning but not by depth of learning.
At the same time it is clear that attendance has an impact on performance. Students who attended lectures and tutorials had a better chance of success on all assessment tasks in particular the final exam (see tables 8 and 9). Successful students attend lectures and tutorials; less successful students may have genuine reasons for non attendance.
Implications
Why should we care? As teachers, should we simply accept that the trend towards non attendance is inevitable, that we are being replaced by technology, our customers no longer need or want us, and we are becoming obsolete? However, the answer is not simply to increase attendance as Rodgers (2002) found. Even though students increased their attendance through an incentive scheme, performance remained the same. Clearly, the quality of the learning experience has to change. Some of us are stubborn enough to think that we may be able to add value in lectures and that just possibly, students may come to gain knowledge rather than information. Maybe it is not about attendance but about better teaching and learning processes.
Philips (2004) questions the traditional, lecture/ tutorial/ examination approach to teaching at university, considers research about learning, and then questions why university teaching and learning practices continue to be resistant to, and often inconsistent with, fundamental principles of learning developed through sustained scholarly enquiry. Some researchers argue that teaching should focus on a 'student-centered learning environment acknowledges that students use current knowledge to construct new knowledge, according to the constructivist epistemology discussed earlier (Duffy & Jonassen 1992; Marra & Jonassen 1993; Reeves & Hedberg 2002). Teachers' espoused theory is constructivist, student-centered, and outcome-based leading to 'deep' learning. While Philips argues that the 'theory-in-use' is instructivist, teacher-centered, content-based leading to surface learning, he questions why many university lecturers do not practice the espoused theory. The answer may lie with the students - are they willing and able to accept responsibility for their learning?
Biggs (1999) found that students who are instrumentally motivated are likely to adopt a surface approach to studying, which does not lead to high quality learning. In Ditcher and Hunter's study (2004), academic staff were surveyed about the impact of student behaviour on learning. This lecturer was concerned that instrumental students were concerned with gathering information, rather than knowledge. The result was an ability to remember but not to think deeply:
They seem far more pre-occupied with figuring out what "they need to know" and getting my notes, than reading independently or synthesising material themselves. This concerns me because we end up training students that are good at regurgitating lecture material, but hopeless at assessing new ideas critically, or even proposing new ideas themselves. (Ditcher and Hunter, 2004, p.5).
Some staff felt that the behaviours of instrumental students were symptomatic of a lack of personal responsibility on the students' part:
It seems to me that the underlying problem is lack of personal responsibility on the part of many students and the impact this has on the entire culture of the University ... In my experience, it is very rare for a student to accept responsibility for themselves [sic] and their learning. (Ditcher and Hunter, 2004, p.5).
Inappropriate attitudes to learning are not innate and invariant. Students develop these attitudes because they have experienced a level of success in educational environments that do not support deep understanding and a 'thirst' for knowledge and understanding. We should recognise that these attitudes exist and put in place environments that support appropriate learning strategies.
Pedagogical approaches to education are shifting from teacher-centred approaches, where the emphasis is on individuals receiving knowledge to student-centred approaches where knowledge is collaboratively constructed through engagement in significant and authentic problems reflecting those encountered in the real world (Herrington & Oliver, (2000). These learning environments can be readily developed across all educational disciplines (cf. Herrington & Herrington, 2006). Students who learn in these environments develop higher order processes or graduate attributes that are demanded by society.
Technology is becoming pervasive in education but its benefits are unclear. If technology is used to mirror and perpetuate traditional forms of pedagogy such as acting as a repository of factual (oral or text) information then at best it will be used as a poor alternative to lectures as it is by many of our current students; at worst it will continue the belief that knowledge is passively transmitted from one individual to another for the sole purpose of memorisation and replication. On the other hand, the affordances of technology can provide the tools for creating authentic learning environments and fostering the communication channels that support the social construction of knowledge and understanding.
But why engage in the learning process if the knowledge for performing successfully can be gained without thought and effort? If our assessment practices rely on replication of factual information and if this is easily gained through passively attending lectures and or headphones attached to my MP3 player then again it is easy to see why some students will not engage. The final piece in the jigsaw and the one most often lost is assessment. If we want students to attend and be rewarded by that attendance then we need to think more carefully about assessment. Instead of the traditional end on approach to assessment we need to integrate our assessment with the tasks by which students learn. The outcome of the learning task becomes the assessment and not some far away facsimile as is often the case with end of semester exams.
In summary, changing students' attitudes and approaches to learning relies on a change in teacher attitudes towards teaching, assessment and technology. A change in students' and teachers' attitudes may well see a resurgence in class attendance.
Appendix 1
Survey Questions
- Which tutorial class did you attend?
- How many tutorials did you attend?
- Why did you miss tutorials? Please indicate how strongly you agree with each of the following statements using the following scale.
Strongly disagree = 1, Disagree = 2, Not sure = 3, Agree = 4, Strongly agree = 5.- I was genuinely sick
- Too busy
- Had to work
- The tutorials were boring (process)
- The topic was boring
- Didn't like the tutor
- I don't like the subject
- Couldn't be bothered
- How many lectures did you attend?
- Why did you miss lectures? Please indicate how strongly you agree with each of the following statements using the following scale.
Strongly disagree = 1, Disagree = 2, Not sure = 3, Agree = 4, Strongly agree = 5.- I was genuinely sick
- Too busy
- Had to work
- Clash with another subject
- The lectures were boring (process)
- The topic was boring
- Didn't like the lecturer
- I don't like the subject
- Couldn't be bothered
- Get the lectures on eduStream
- I can get through the subject without going to lectures
- Lectures are a waste of time
- Please add any comments you wish to make on why you didn't attend lectures in this subject
- Do you think having lectures available on eduStream is a good thing? Yes/No
- Why do you feel that way?
Appendix 2
Class Participation
The following is extracted from the 2005 Subject Outline for MGMT389 International Business Management.
Assessment 2: |
Title: CLASS PARTICIPATION |
|---|---|
Guidelines |
Students will be required to actively participate in the subject. Class participation includes contribution to class discussion including questions, comments, reflection, sharing experiences and feelings, and feedback on Case Study presentations. The specific criterion explaining this assessment is provided in the section on assessment criteria that follows. Students will be awarded a grade out of 5 marks for the subject for class participation. |
Classification |
This is a category 3 assignment. Refer to guidelines at the end of this subject outline. |
Marking criteria |
Students that attend all tutorials and actively participate will be awarded 5/5. By active participation, we mean you are involved in the discussion, either by posing questions, making comments or observations that contribute to the learning process. We are more interested in the quality of comments rather than quantity, so we would classify two or three insightful comments per class as an active contribution. Students that miss one or two classes but are still actively involved will be awarded 4/5. Students that attend all classes but only contribute occasionally will be awarded 3/5. Students that attend only the minimum number of classes (i.e. 75%) but contribute when in attendance will be awarded 2/5. Students that attend only the minimum and occasionally contribute will be awarded 1/5. Students that attend the minimum and do not contribute will be awarded 0/5. |
Length: |
Participation in tutorials |
Weighting: |
5% |
Due date |
Grades will be awarded at the completion of the tutorials |
References
Australian Vice-Chancellors' Committee (2001). Key Statistics on Higher Education.
Beard, R. & Senior, I. (1980). Motivating Students. London: Routledge and Kogan Paul.
Biggs, J. (1999). Teaching for quality learning at University. Buckingham, UK: Society for Research into Higher Education & Open University Press.
Bligh, D. A. (1972). What's the Use of Lectures. Harmondsworth, UK, Penguin.
Bliss, J. and Ogborn, J. (eds.) (1977) Students' Reactions to Undergraduate Science. London: Heinemann.
Brown, G. and Atkins, M. (1988) Helping Students Learn. In Effective Teaching In Higher Education. London: Routledge.
Browne, S. and Race, P. (2002) Lecturing: A Practical Guide. London: Kogan Page.
Coxon, E., Jenkins, K., Marshall, J. & Massey, L. (1994). The politics of learning and teaching in Aotearoa - New Zealand. Palmerston North, NZ: Dunmore Press.
Devados, S. and Foltz, J. (1996), Evaluation of Factors Influencing Student Class Attendance and Performance, American Journal of Agricultural Economics, Vol. 78, No. 3, pages 499-507.
Ditcher, A. and Hunter, S. (2001). The instrumental student: An increasing problem? In L. Richardson and J. Lidstone (Eds), Flexible Learning for a Flexible Society, 202-212. Proceedings of ASET-HERDSA 2000 Conference, Toowoomba, Qld, 2-5 July 2000. ASET and HERDSA.
Dolnicar, S. (2004), What Makes Students Attend Lectures? The Shift Towards Pragmatism in Undergraduate Lecture Attendance, In Australian and New Zealand Marketing Academy - ANZMAC 2004: marketing accountabilities and responsibilities : proceedings: 29 November - 1 December 2004, Wellington', edited by J Wiley and P Thirkell, Wellington, N.Z.
Duffy, T. M. and D. H. Jonassen, (Eds). (1992). Constructivism and the Technology of Instruction, A Conversation,. New Jersey, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Durden, C. & Ellis, L. (1995). The effects of attendance on student learning in principles of economics. The American Economic Review, 85(2), 343-346.
Doulai, P. (1999), Preserving the Quality of On-Campus Education using Resource-Based Approaches, In Proceedings of the WebCT Conference on Learning Technologies: From Innovation to Implementation (WebCT'99), pages 97-101, Vancouver, Canada, June 1999.
Exley, K. and Dennick, R. (2004) Giving a Lecture: From Presenting to Teaching. London: Routledge.
Feldman, K.A. (1976), The Superior College Teacher from the Students' View. Research in Higher Education, 30: 583-645.
Feldman, K.A. (1989), The Association Between Student Ratings of Specific Instructional Ratings of Specific Instructional Dimensions and Student Achievement. Research in Higher Education, 30: 583-645.
Herrington, J., & Oliver, R. (2000). An instructional design framework for authentic learning environments. Educational Technology Research and Development, 48, 23-48.
Herrington, A.J., & Herrington, J.A. (2006). Authentic Learning Environments in Higher Education. Hershey, PA: Idea Group.
Isaacs, G. (1992) Ends and Means: What Learning Goals are Served by What Methods? Research and Development in Higher Education, 15: 205-212.
Land, M.L. (1985) Vagueness and Clarity in the Classroom. In T. Husen and T. N. Postlethwaite (Eds.) International Encyclopaedia of Education: Research Studies. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Laurillard, D. (1993) Rethinking University Teaching: A Conversational Framework. London: Routledge.
Marra, R. and D. Jonassen (1993). Whither Constructivism. In D. Ely, Minor, B. (Ed.) Educational Media and Technology Yearbook. (pp. 56-77) Englewood CO, Libraries Unlimited, Inc. Published in cooperation with ERIC and AECT.
Marburger, D.R. (2001), Absenteeism and Undergraduate Exam Performance, Journal of Economic Education, Vol 32. No. 2, pages 99-109.
Marton, F., & Säljö, R. (1976). On qualitative differences in learning. I: Outcome and process. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 46, 115-27.
McInnis, C., & Hartley, R. (2002). Managing Study and Work: The impact of full-time study and paid work on the undergraduate experience in Australian universities. Department of Education, Science and Training, Commonwealth of Australia.
McKeachie, W. (1994) Teaching Tips. Lexington: Heath.
Murphy, E. (1998) Lecturing at University. Perth: Paradigm Books.
Naber, L. and Köhle, M. If e-Learning is the Answer, what was the Problem? Institute for Software Engineering and Interactive Systems, Vienna University of Technology,
Phillips, R. (2005), Challenging The Primacy Of Lectures: The Dissonance Between Theory And Practice in University Teaching, Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice, Vol. 2, Iss. 1.
Podcastingnews (2005). Purdue Plans Academic Podcasts http://www.podcastingnews.com/archives/2005/08/purdue_plans_ac.html [Accessed 16/10/05]
Race, P. (Ed.) (2002) 2000 Tips for Lecturers. London: Kogan Page.
Ramsden, P. (1992) Learning to Teach in Higher Education. London: Routledge.
Reeves, T. C., & Hedberg, J. G. (2002). Interactive Learning Systems Evaluation. Educational Technology Press.
Rodgers, J.R. (2001), A panel-data study of the effect of student attendance on university performance, Australian Journal of Education, Vol. 45, No. 3, 2001, 284-295.
Rodgers, J.R. (2003). Encouraging tutorial attendance at university did not improve performance. Australian Economic Papers, 41, 255-256.
Rodgers, J.L. and Rodgers, J.R. (2003), An Investigation into the Academic Effectiveness of Class Attendance in an Intermediary Microeconomic Theory Class, Education Research and Perspectives, Vol. 30. No.1.
Romer, D. (1993), Do Students Go to Class? Should They? Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 7 No. 2, pages 167-174.
Sheffield, E.F. (1974) Teaching in Universities: No One Way. Montreal: Queen's University Press.
Solomon, D. Rosenberg, L. and Bezdek, W.D. (1964) Dimensions of Teacher Behaviour. Journal of Experimental Education, 33: 23-401.
Snyder, B. (1971). The hidden curriculum. Cambridge: MIT Press.